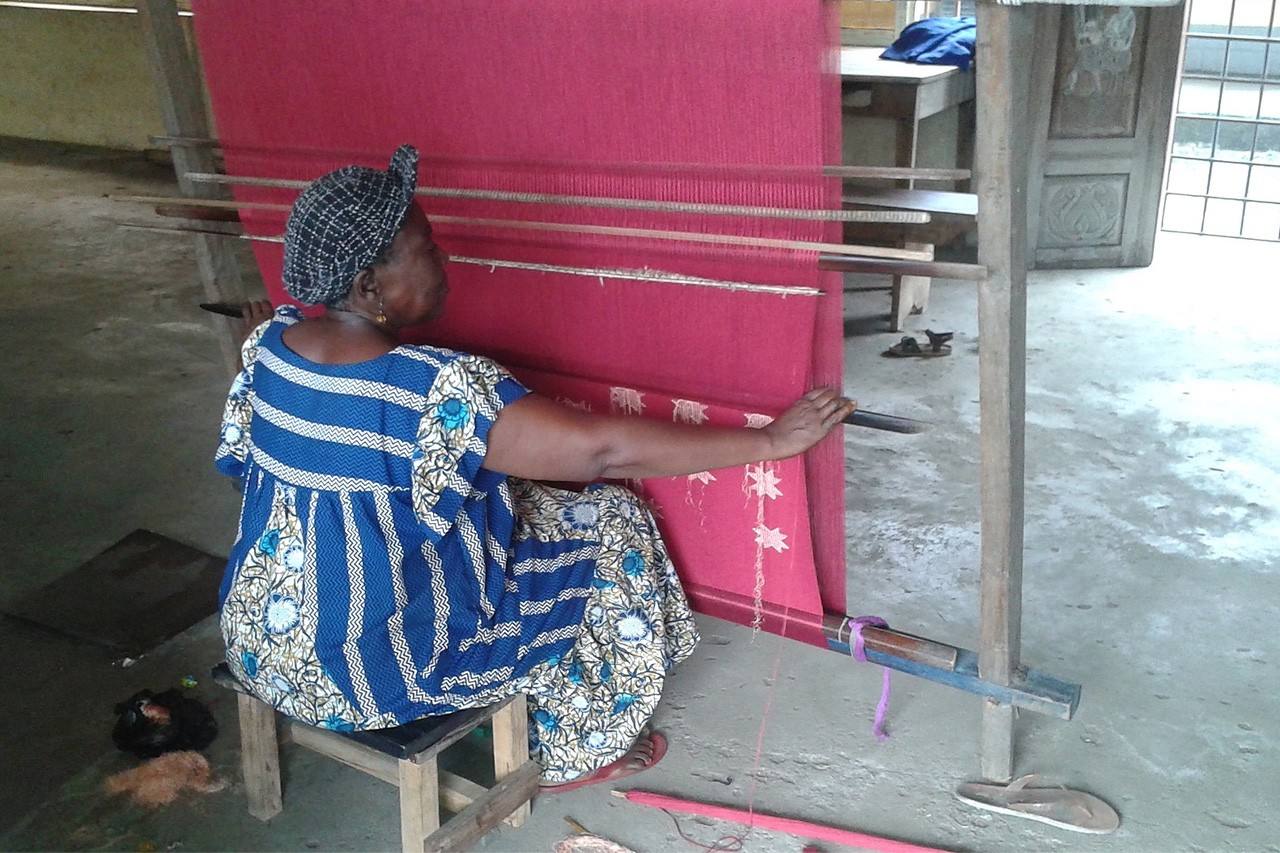
Akwete fabric makers must mechanize quickly—the Chinese are coming
So, how can local Akwete fabric producers get adequate training to replace antiquated manual labor methods with competitive contemporary machines and mechanisms?

Culled from the Texas International Guardian
The new governor of Anambra State, Chukwuma Charles Soludo, may have set in motion what might be perceived as the second revolution of Akwete textiles. Throughout his campaign, and as recently as today, he has not just preached this philosophy but has also demonstrated it by voluntarily offering himself as this local trade’s brand ambassador. According to the governor, “My Akwete dress is not just a dress; it’s a statement. I want to make a statement with it. You know, in the entire Southeast, this is the only textile product alive, and it’s handmade by the women of Akwete in Abia State.”
Soludo’s proclamation soon aroused other leaders in the Southeast to follow suit and advocate a similar cause―to revitalize and purchase these local textiles. A few days ago, Governor Okezie Ikpeazu of Abia (Akwete’s home state) and other governors attending the People’s Democratic Party (PDP) Governors’ Forum wore Akwete fabrics to their meeting in the Ukwa East local government area.
Governor Ikpeazu has always been a fan of this fabric and has always expressed pride that it comes from his home state. Other political and community leaders and celebrities of Igbo descent have also used this fabric to demonstrate loyalty.
However, the purpose of this commentary is not to assess the people’s benefaction of, or devotion to, this product. By all indications, this product and the makers have now been given another chance to prosper from their handicraft once again. Igbos, it appears, are passionately ready to make this fabric their signature attire. One may recall that Akwete fabric textiles thrived during the nineteenth century and were worn by the women of Akwete (now Abia State). The Igbos then started trading this fabric for goods from international traders and those from other parts of Nigeria.
Online commerce has extensively superseded traditional face-to-face or business-to-business trade engagements
Currently, however, the Akwete production technique is not very different from what it was when it began. The weaving involves a laborious, manual interlacing technique performed on a two-system loom. Weavers sit on a low chair, and they labor for hours to produce a substantial length. Today, however, the global system has completely changed, and the economic environment is entirely different. Online commerce has extensively superseded traditional face-to-face or business-to-business trade engagements.
Remember, Akwete clothmakers are local, traditional fabricators who do not know about branding their talents nor elevating them to a competitive market level. They are, therefore, likely to lose their entire Akwete fabric culture to larger, capital-oriented companies from other places. It’s possible that while wearing this fabric at political events or in loyalty to a homemade product is healthy for promotion and ancestry comradeship, it might bear no economic relevance.
Currently, there have been attempts by a few Nigerian traders and investors to develop a more modernized fabrication system, but that might not be enough to sustain the modern global market structure. For instance, with China’s advent as a significant player in Africa, trade and investment have grown tremendously. China now competes with the United States and European Union (EU) as one of Africa’s trade, investment, and aid partners. They are all over Africa buying up ideas and exploring products and cultures—and then commercializing them through predatory monopolistic ventures.
Globally, the fabric industry is strong. Unfortunately, African fabric dealers and manufacturers remain vulnerable to more aggressive, well-prepared foreign merchants. For example, Qingdao Phoenix, a Chinese textile industry specializing in African wax printing materials, touts the most advanced equipment and latest technologies in textile production. This company is also the manufacturer of the Hitarget brand, which features what are considered to be the most popular African print designs, styles, and colors. Interestingly, most Dutch designs available today within the African marketplace are low-cost reproductions made in China.
Akwete challenge is beyond a trending “made-in-Abia” excitement
Therefore, the Akwete challenge is beyond a trending “made-in-Abia” excitement. It is now a matter of urgency to facilitate the strategic transition from creating these products by hand to using relevant technologies. This philosophy must go beyond looking at who wears these fabrics or does the photoshoot; training, capital investment, and other appropriate support efforts are necessary to initiate technological innovation and process change.
So, how can local Akwete fabric producers get adequate training to replace antiquated manual labor methods with competitive contemporary machines and mechanisms? How can they embrace relevant technologies to distribute and market this product and eliminate the current, outdated business-to-consumer sales and distribution culture? How sincerely do they want to remain producers, distributors, or perhaps sole custodians of their talent and artistic culture—without losing out to today’s ruthless, capitalistic market environment?
Grab a coffee, and let’s have a conversation. #
♦Publisher of the Guardian News, Professor Anthony Obi Ogbo, Ph.D. is on the Editorial Board of the West African Pilot News. He is the author of the Influence of Leadership (2015) and the Maxims of Political Leadership (2019). Contact: anthony@guardiannews.us
- War Notes On A Biafran Night - April 17, 2022
- Mechanizing Akwete fabric makers - April 17, 2022
 +281-788-8133
+281-788-8133